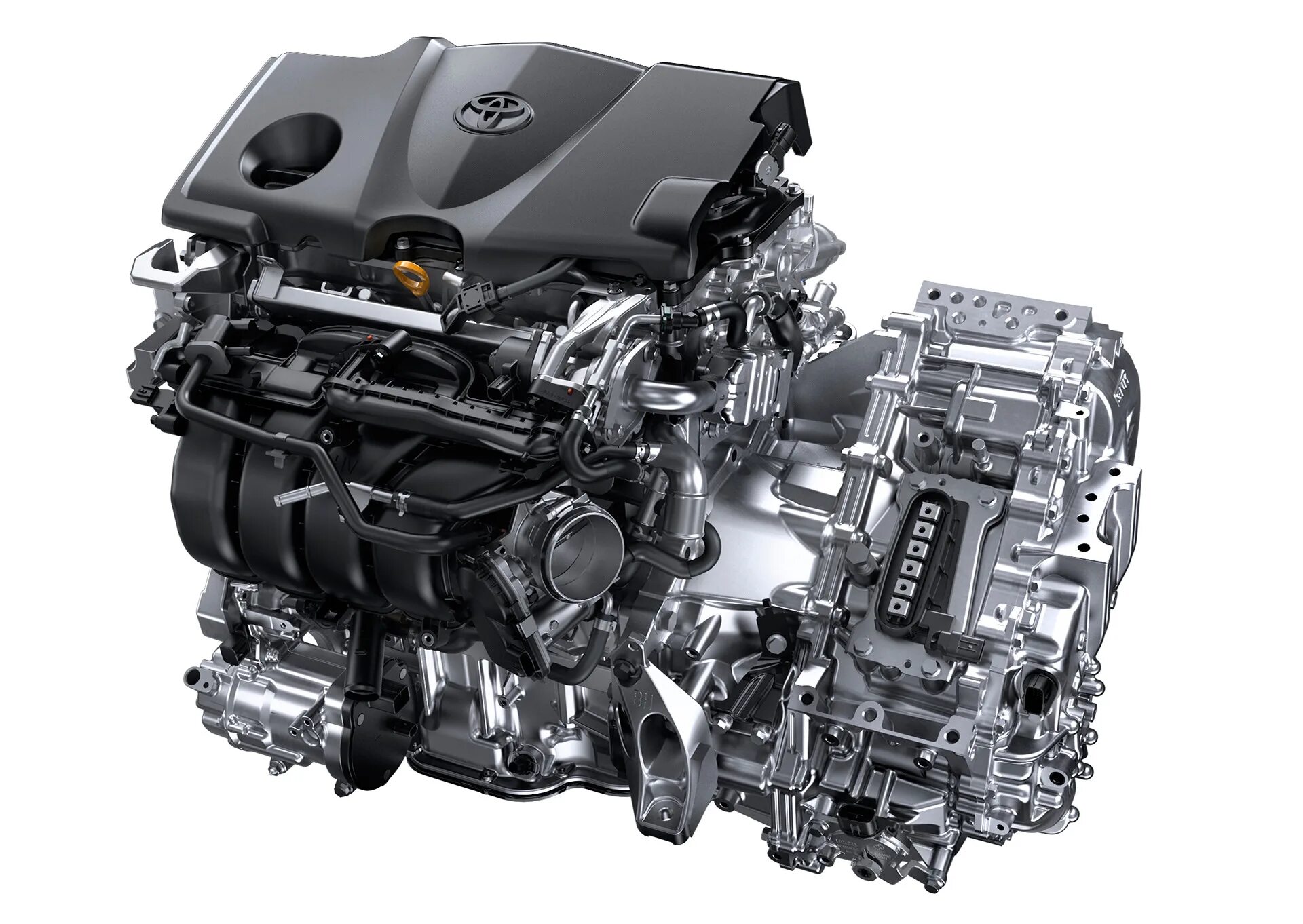
Why It’s Great: Ultra-efficient small hybrid engine — not yet common in North America but sets the benchmark for small-car fuel economy.
Contents
- 1 Toyota 1.8L Atkinson-Cycle (2ZR-FXE) Engine
- 2 Honda 1.5L Turbocharged Engine (L15B7)
- 3 Mazda 2.0L SkyActiv-G
- 4 Hyundai 1.6L Smartstream (GDI/MPi Hybrid)
- 5 Toyota 2.5L Dynamic Force (A25A-FXS Hybrid)
- 6 GM 1.0L & 1.4L Turbo Ecotec (L3T & LE2)
- 7 Ford 1.0L EcoBoost (3-Cylinder)
- 8 Toyota 1.5L Dynamic Force (M15A-FXE)
- 9 Comparison of Most Efficient Gasoline & Hybrid-Friendly Engines
- 10 Awards and Recognitions from Leading Automotive Authorities
Toyota 1.8L Atkinson-Cycle (2ZR-FXE) Engine
The Toyota 2ZR-FXE is a 1.8-liter inline-4 engine designed specifically for hybrid vehicles. It is part of Toyota’s ZR engine family and operates using the Atkinson cycle, a thermodynamic process that improves efficiency by allowing the intake valve to remain open longer during the compression stroke. This results in reduced pumping losses and significantly improved fuel economy, particularly in stop-and-go urban environments.
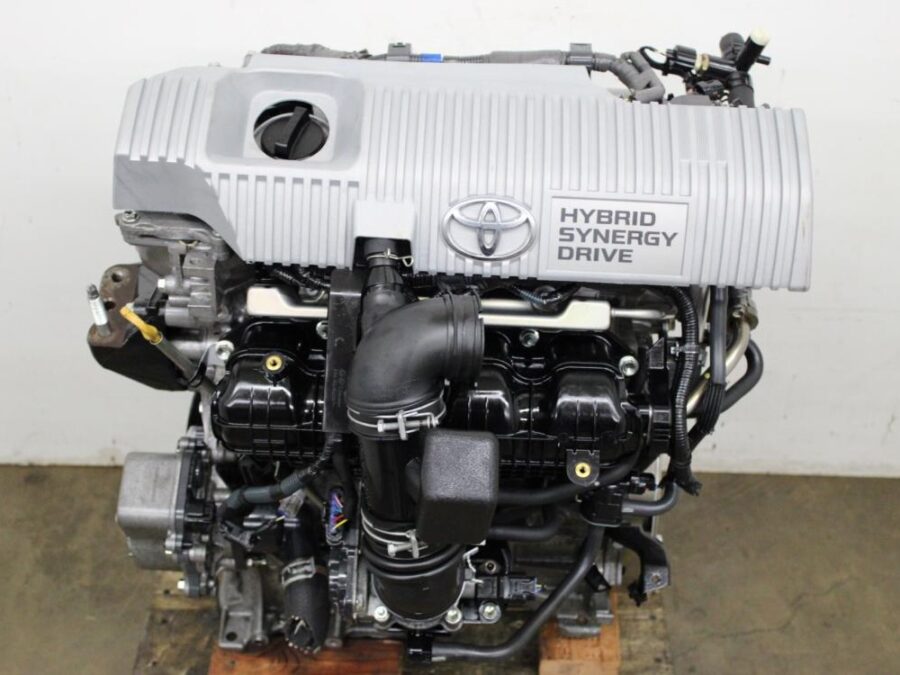

Engine Specifications
| Engine Code | 2ZR-FXE |
|---|---|
| Displacement | 1.8 liters |
| Configuration | Inline-4 |
| Compression Ratio | 13.0:1 |
| Fuel System | Port fuel injection, Dual VVT-i |
| Cycle | Atkinson |
| Thermal Efficiency | Over 40% |
| Horsepower | Approx. 98 hp (engine only) |
Applications
The 2ZR-FXE powers a wide range of Toyota hybrid models, including the Prius (from the third generation onward), the Corolla Hybrid, and the Lexus CT 200h. It also appears in some international models such as the Toyota Aqua (also known as Prius c).
Real-World Efficiency
In real-world driving, the engine delivers exceptional fuel economy when paired with Toyota’s Hybrid Synergy Drive system. For example, the Prius achieves up to 58 MPG in city driving and over 50 MPG combined, depending on the model year and trim. The Corolla Hybrid also returns impressive numbers, often exceeding 52 MPG combined.
Why It’s Special
Unlike traditional Otto cycle engines, the 2ZR-FXE sacrifices some power output in favor of efficiency and longevity. It features an extremely simplified design optimized for low emissions and high reliability. The Atkinson cycle and hybrid integration allow the engine to run at its most efficient RPM range most of the time. Additionally, its longevity is well documented, with many Prius models reaching over 300,000 miles on the original powertrain.
The Toyota 2ZR-FXE is a benchmark in hybrid engine technology. Its balance of reliability, efficiency, and simplicity makes it a standout in the world of internal combustion engines. While it may not be a powerhouse, its ability to deliver long-term savings at the pump and on maintenance costs cements its status as one of the most efficient and dependable small engines in modern automotive history.
Honda 1.5L Turbocharged Engine (L15B7)
The Honda L15B7 is a 1.5-liter inline-4 turbocharged engine that belongs to Honda’s “Earth Dreams Technology” engine family. It is one of the most widely used engines across Honda’s modern lineup and has gained a reputation for its impressive balance of performance and fuel economy. The engine features direct injection and variable valve timing, allowing it to deliver a strong driving experience while maintaining excellent real-world efficiency.
Engine Specifications
| Engine Code | L15B7 |
|---|---|
| Displacement | 1.5 liters |
| Configuration | Inline-4, Turbocharged |
| Fuel System | Direct Injection, Dual VTC |
| Horsepower | 174–205 hp (varies by model) |
| Torque | 162–192 lb-ft |
| Compression Ratio | 10.3:1 |
| Fuel Type | Regular Unleaded (87 Octane) |
The L15B7 engine is used in a wide range of Honda vehicles, including the Civic (EX, Touring, Si trims), CR-V, Accord (base trims), and HR-V. It represents Honda’s shift toward downsized, turbocharged engines in response to stricter emissions and fuel economy standards.
Efficiency and Real-World Fuel Economy
Despite being turbocharged, the L15B7 is capable of delivering exceptional fuel economy when driven conservatively. In the Honda Civic, EPA ratings range from 32 to 42 miles per gallon on the highway, depending on the model and trim. The CR-V equipped with this engine also performs well, averaging around 34 MPG on the highway.
Notable Features and Engineering
One of the defining characteristics of the L15B7 is its low-end torque and responsiveness, thanks to its turbocharger. Honda engineers also integrated a variable valve timing system (VTC) and a single-scroll turbo to maintain simplicity and durability. While early versions of this engine in cold climates faced issues with oil dilution due to fuel mixing with oil, Honda has since addressed these issues with ECU updates and design tweaks.
Why It Stands Out
The L15B7 successfully combines the fuel-saving benefits of a small displacement engine with the power of a turbocharger. It’s versatile enough to power everything from sporty Civics to compact SUVs. When properly maintained and kept up to date with Honda’s service campaigns, this engine delivers excellent reliability and efficiency, making it a smart choice for drivers who want performance and economy in one package.
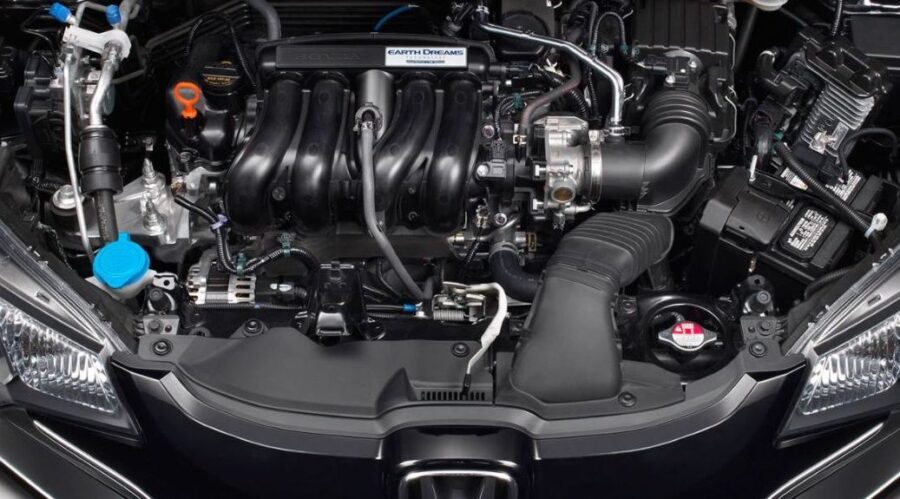

Dual Injection System (GDI + MPi)
The Honda 1.5L L15B7 engine stands out as one of the best examples of modern turbocharged engineering in the compact segment. It offers strong fuel economy, respectable performance, and long-term reliability — especially in post-2019 models where early technical concerns have been resolved. It’s a cornerstone in Honda’s push for cleaner, more efficient internal combustion engines that don’t compromise the fun-to-drive factor.
Mazda 2.0L SkyActiv-G
| Vehicles | Mazda3, Mazda CX-30 |
|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Up to 41 mpg highway |
| Compression Ratio | 13.0:1 – 14.0:1 (depending on market) |
| Induction | Naturally Aspirated (no turbo/supercharging) |
High Compression for Lean Combustion
The heart of the SkyActiv-G’s efficiency lies in its unusually high compression ratio. At 13:1 in the U.S. and up to 14:1 in Japan, this is one of the highest compression ratios seen in a mass-market gasoline engine. A higher compression ratio allows the engine to extract more energy from the combustion process. This increases thermal efficiency — more power from the same amount of fuel — and directly reduces fuel consumption.
Combustion Chamber Optimization
Mazda reshaped the piston head and the combustion chamber to ensure fuel and air mix more evenly. This design leads to more complete combustion, which improves both power and fuel economy. The location and spray pattern of the fuel injectors are engineered to reduce knocking (pre-ignition), which is usually a risk in high-compression engines.
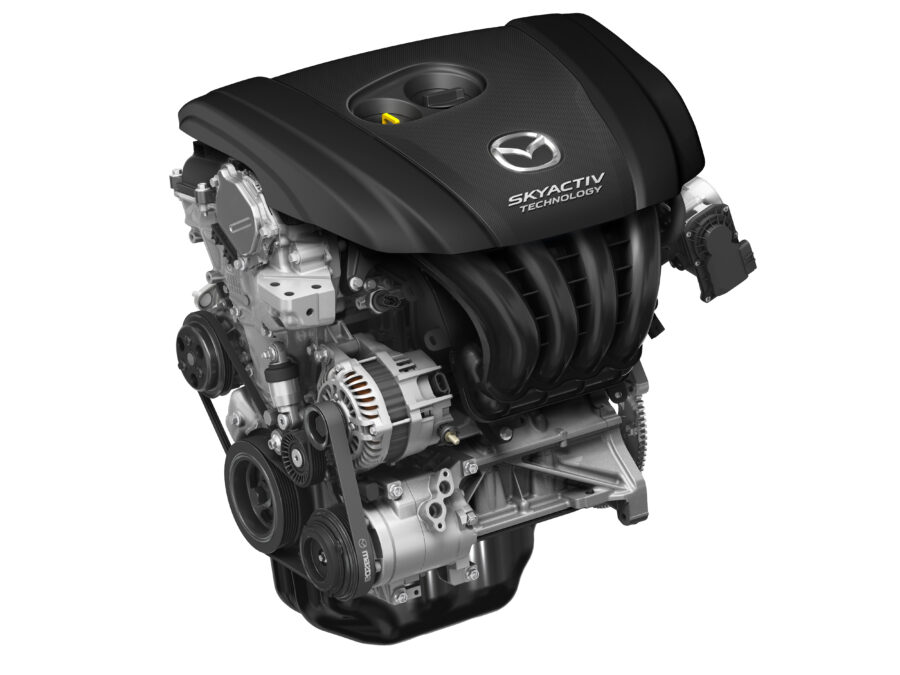

Reducing Internal Friction
SkyActiv engines use lighter materials and tighter machining tolerances to reduce resistance within the engine. Components like pistons, crankshafts, and connecting rods are engineered to move more freely, which means less energy is lost to friction and more is converted into usable power. Mazda also uses low-friction oil seals and coatings.
Long Stroke Design
Mazda employs a “long-stroke” engine design — meaning the piston travels a longer distance up and down within the cylinder. This helps burn fuel more efficiently and improves low-end torque, which is helpful for city and highway cruising alike. It also allows the engine to operate at lower RPMs, which saves fuel.
Light Vehicle Weight + Transmission Pairing
Another factor that complements this engine is Mazda’s insistence on keeping vehicle weights down and using efficient automatic and manual transmissions (like the SkyActiv-Drive 6-speed). These transmissions are tuned for early upshifts and minimal energy loss, ensuring the engine can operate in its optimal range as often as possible.
Why It’s Impressive
The Mazda 2.0L SkyActiv-G is a rare example of a naturally aspirated engine delivering hybrid-like fuel economy. It does so without turbocharging, electric assistance, or exotic materials — relying instead on elegant engineering and combustion science. For drivers who want simplicity and long-term reliability with low fuel costs, this engine stands out.
Hyundai 1.6L Smartstream (GDI/MPi Hybrid)
| Vehicles | Hyundai Elantra Hybrid, Kia Niro |
|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Up to 54 mpg combined |
| Fuel System | Dual Injection (Gasoline Direct + Multi-Point) |
| Engine Cycle | Atkinson Cycle |
| Hybrid Components | Electric Motor, Lithium-ion Battery, 6-speed DCT |
Atkinson Cycle for Efficiency Over Power
Unlike traditional Otto-cycle engines, this 1.6L uses the Atkinson cycle — a thermodynamic process that leaves the intake valve open longer during compression. This reduces pumping losses and allows for a more fuel-efficient, albeit less powerful, combustion. It’s ideal for hybrids because the electric motor compensates for the torque loss, providing smooth acceleration while the gasoline engine focuses on sipping fuel.

The Smartstream engine uses both Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) and Multi-Point Injection (MPi), intelligently switching between them based on load and speed. GDI provides precision and power under heavy demand, while MPi helps clean the intake valves and improves efficiency during low-load conditions. The result is cleaner combustion, lower emissions, and improved long-term engine health.
Integration with Electric Motor & Hybrid System
This engine works in tandem with a compact electric motor powered by a lithium-ion polymer battery. The hybrid control system manages energy flow between the engine, electric motor, and battery, choosing the most efficient power source based on conditions. In city driving, the car can operate entirely on electric power at low speeds, while the engine engages seamlessly when needed.
Regenerative Braking and Start/Stop Technology
Hyundai’s hybrid system includes regenerative braking — capturing kinetic energy during deceleration and converting it into electricity to recharge the battery. This reduces the load on the gasoline engine. Idle Stop & Go (ISG) technology shuts off the engine at stoplights and automatically restarts it when the driver lifts off the brake, preventing fuel waste during idling.
6-Speed Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT)
Unlike many hybrids that use a CVT (continuously variable transmission), Hyundai pairs this engine with a 6-speed dual-clutch automatic. This provides a more engaging, traditional driving feel while offering excellent efficiency thanks to its quick, low-loss gear changes. The transmission is optimized to shift early and keep the engine in its most efficient RPM band.
Why It’s Impressive
The 1.6L Smartstream hybrid powertrain is a showcase of balance — blending combustion efficiency with electric power and a driver-friendly gearbox. It achieves incredible fuel economy without the rubber-band feel of a CVT, and the use of proven technologies like the Atkinson cycle and regenerative braking makes it both effective and reliable. It’s one of the best examples of how hybrid systems can optimize gasoline engines for modern-day driving without compromise.
Toyota 2.5L Dynamic Force (A25A-FXS Hybrid)
| Vehicles | Toyota Camry Hybrid, RAV4 Hybrid, Lexus ES 300h |
|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Up to 52 mpg combined (Camry Hybrid) |
| Thermal Efficiency | Up to 41% |
| Engine Cycle | Atkinson Cycle |
| Fuel Injection | D-4S Dual Injection (Direct + Port) |
High Compression and Long Stroke Architecture
The A25A-FXS engine is designed with a high compression ratio of 14.0:1, enabling more complete combustion of the air-fuel mixture. Combined with a long-stroke layout, the engine extracts more energy per combustion event. This design improves low-end torque while keeping fuel consumption low, especially under light-load cruising conditions where hybrids often operate.
Advanced Fuel Delivery with D-4S Injection
Toyota’s D-4S system combines direct and port fuel injection. Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber for precision and power, while port injection ensures intake valve cleanliness and smoother operation at low loads. The ECU constantly adjusts the mix between both systems depending on conditions, which contributes to better fuel atomization, reduced knocking, and improved thermal efficiency.

Hybrid Synergy Drive Integration
The engine operates as part of Toyota’s proven Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD). At lower speeds or light throttle, the vehicle can run on electric power alone. Under acceleration or hill climbing, the gasoline engine activates smoothly and assists the motor. The system prioritizes electric drive when possible and uses the engine primarily for maintaining speed and recharging the battery during coasting or braking.
Electric Motor Assist and Regeneration
Toyota’s hybrid system includes a powerful electric motor-generator setup that helps both propel the vehicle and regenerate energy. During braking, kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy and stored in the battery. This reduces the need for fuel-derived power and further enhances city fuel economy. The electric motor also helps launch the vehicle from a stop, reducing the load on the gasoline engine.
Engine Warm-Up and Efficiency Management
To maximize efficiency, Toyota has engineered a rapid warm-up phase for the engine. A variable coolant flow system and electric water pump reduce parasitic losses and help bring the engine to operating temperature faster, where it performs most efficiently. Once warmed, the hybrid control unit carefully modulates engine engagement to minimize unnecessary fuel burn.
Why It’s Exceptional
This 2.5L Dynamic Force engine isn’t just about power — it’s about precision and control. Achieving thermal efficiency figures over 40%, it rivals some diesel engines in terms of combustion effectiveness. Paired with a hybrid system that can intelligently alternate between electric and gas power, it delivers not only outstanding economy but also long-term reliability and smoothness that Toyota is known for.
GM 1.0L & 1.4L Turbo Ecotec (L3T & LE2)
| Vehicles | Chevy Spark, Sonic, Cruze |
|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Up to 39 mpg highway |
| Engine Type | Inline-3 (1.0L) / Inline-4 (1.4L), Turbocharged |
| Fuel System | Direct Injection |
| Transmission Pairing | Best with 5/6-speed Manual |
Turbocharging for Low-End Torque
Both the 1.0L and 1.4L Ecotec engines use a small single-scroll turbocharger to boost performance, especially at low RPM. This allows the engine to produce torque that would typically require a much larger displacement. In urban driving, where stop-and-go traffic dominates, the extra torque helps the car move with ease without needing to rev the engine hard — which saves fuel.
Compact Displacement and Lightweight Internals
Smaller engines naturally use less fuel, but GM goes further by using lightweight components like hollow camshafts, forged crankshafts, and compact aluminum blocks. These choices reduce internal inertia and friction, allowing the engine to spin more freely and operate efficiently across a wide range of speeds. Lower weight also contributes to improved vehicle efficiency overall.

Direct Injection with Knock Control
To maintain efficiency under pressure, both engines use direct injection for precise fuel delivery. Injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber enables higher compression and better control of the combustion event. GM integrates advanced knock control algorithms and ion-sensing spark plugs to monitor combustion in real time, adjusting timing and boost to stay in the most efficient range without damaging the engine.
Low-Pressure Exhaust Gas Recirculation (LP-EGR)
An important efficiency tool in these engines is the use of LP-EGR, where a portion of cooled exhaust gas is reintroduced into the combustion chamber. This lowers peak combustion temperatures, reduces the production of NOx emissions, and allows for more aggressive timing and leaner air-fuel mixtures — all of which contribute to fuel economy without sacrificing driveability.
Transmission Tuning and Manual Advantage
While these engines are offered with automatic options, they perform best when paired with a manual transmission. Manual gearboxes allow the driver to keep engine RPMs in the most efficient range, especially during highway cruising. GM tunes final drive ratios and shift logic in automatic versions to optimize efficiency, but the light throttle response of the manual gives the greatest benefit for mileage-conscious drivers.
Why It’s Clever
The 1.0L and 1.4L Ecotec engines are not hybrids, yet they manage to deliver economy figures that approach hybrid territory — especially when driven gently. Their strength lies in thoughtful turbo tuning, low internal resistance, and clever calibration. For drivers who enjoy engaging with the car via a manual shifter and prioritize affordability, these engines hit a sweet spot between efficiency, simplicity, and decent real-world performance.
Ford 1.0L EcoBoost (3-Cylinder)
| Vehicles | Ford Fiesta, Ford Focus (Europe), Ford EcoSport |
|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Up to 40 mpg highway |
| Engine Layout | Inline-3, Turbocharged |
| Displacement | 999 cc |
| Key Technologies | Turbocharging, Direct Injection, Variable Valve Timing, Cylinder Deactivation (select versions) |
Turbocharging to Maximize Output
Ford’s 1.0L EcoBoost uses a compact, low-inertia turbocharger that delivers quick boost at low RPM. This enables the engine to produce power levels that rival 1.6L or 1.8L naturally aspirated engines, while consuming far less fuel. The turbo works in harmony with precise engine mapping to deliver smooth torque from very low engine speeds, improving both city and highway efficiency.
Direct Injection and Precise Fuel Management
Fuel is delivered via high-pressure direct injection, which atomizes gasoline directly into the combustion chamber. This system gives Ford tight control over the timing, volume, and shape of the combustion event, allowing for leaner mixtures and optimized ignition timing. The end result is cleaner combustion and better thermal efficiency with minimal waste.
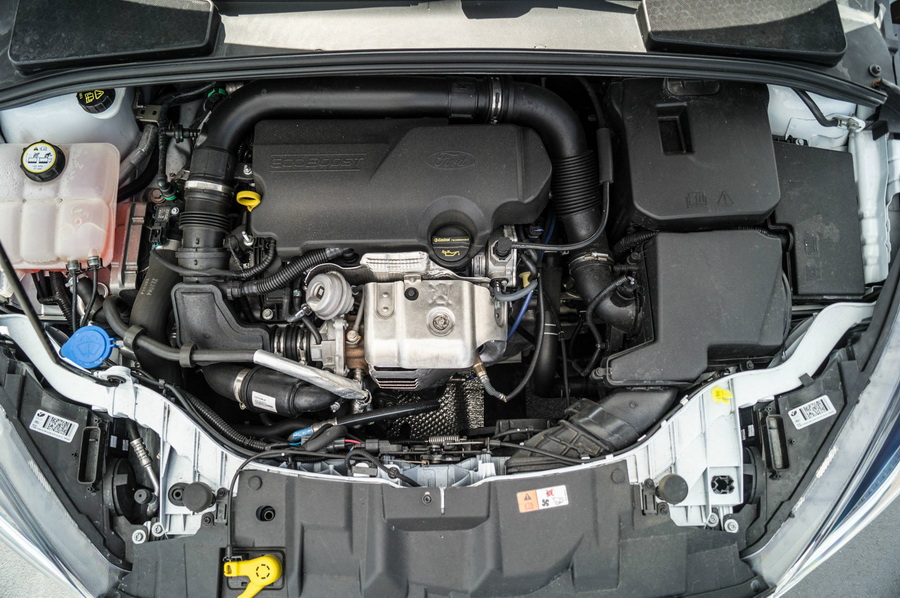
Three-Cylinder Configuration for Reduced Friction
With only three cylinders, there are fewer moving parts, which means less internal friction and mechanical drag. Ford also strategically balances the engine using a counter-rotating flywheel and engine mounts to cancel out the natural imbalance of a 3-cylinder layout. This allows the engine to maintain smoothness while keeping rotational resistance low — a major contributor to its fuel economy.
Compact Design and Low Mass
The entire engine is small enough to fit on an A4 sheet of paper when viewed from above. Ford made use of aluminum components and integrated the exhaust manifold into the cylinder head, reducing the engine’s weight and enabling quicker warm-up times. A lighter engine not only improves vehicle handling but also reduces the energy required to accelerate, improving efficiency in stop-and-go traffic.
Cylinder Deactivation on Select Versions
In some newer versions of the EcoBoost 1.0L, Ford added cylinder deactivation — a rare feature for 3-cylinder engines. Under light loads, one cylinder temporarily shuts off, effectively reducing fuel consumption by up to 6% during cruising. This technology works seamlessly and helps the engine stretch its efficiency even further on the highway.
Why It Punches Above Its Weight
Ford’s 1.0L EcoBoost is a textbook case of doing more with less. It provides the torque and response of a much larger engine while using fuel more like a hybrid. Thanks to its innovative engineering — from turbo optimization to friction-reducing architecture — it’s one of the most successful small-displacement engines in modern cars. It proves that clever packaging and smart tech can make a tiny engine feel like a heavyweight contender.
Toyota 1.5L Dynamic Force (M15A-FXE)
| Vehicles | Toyota Yaris Hybrid, Toyota Aqua (Japan), Yaris Cross (Europe) |
|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Up to 60+ mpg in real-world city driving (Europe/Japan) |
| Displacement | 1,490 cc (1.5L) |
| Engine Type | 3-cylinder, Atkinson Cycle |
| Thermal Efficiency | Up to 40% |
| Hybrid System | 4th Generation Toyota Hybrid System (THS) |
Atkinson Cycle Efficiency with Small Displacement
The M15A-FXE engine is built on the Atkinson cycle, where the intake valve remains open longer during the compression stroke. This reduces pumping losses and increases efficiency, especially during low-load conditions common in city driving. Pairing this design with a small 1.5L three-cylinder layout means fewer internal losses, less weight, and optimal thermal efficiency for stop-and-go urban environments.
Optimized for Hybrid Synergy
This engine is engineered to work hand-in-hand with Toyota’s fourth-generation hybrid system. It operates at its most efficient RPMs while the electric motor handles transient demands and low-speed operation. The seamless transition between electric and gasoline power means the internal combustion engine is only used when most effective, significantly reducing overall fuel consumption and emissions.

Three-Cylinder Compactness and Balance
While three-cylinder engines naturally have more vibration than four-cylinders, Toyota counteracts this with a precisely balanced crankshaft and strategic engine mounting. The smaller cylinder count reduces mass and mechanical drag, and the reduced surface area means less heat loss — a key contributor to the high thermal efficiency of over 40%.
High Compression and Fast Combustion
With a compression ratio near 14:1, this engine pushes air-fuel mixtures through a carefully shaped combustion chamber that promotes tumble flow — a swirling effect that ensures rapid and complete burning. This design leads to better thermal efficiency, cleaner combustion, and improved responsiveness without increasing emissions.
Paired with E-CVT and Regenerative Braking
The transmission is an electronic continuously variable transmission (e-CVT), which uses planetary gears and electric motors rather than belts and pulleys. It provides smooth, optimal gear ratios while enabling regenerative braking. Energy recovered from deceleration is stored in the battery and reused for electric drive or assist, minimizing wasted energy.
Why It Sets the Benchmark
The M15A-FXE is a masterclass in small engine design. It takes everything Toyota has learned from two decades of hybrid development and condenses it into a light, compact, ultra-efficient package. With real-world fuel economy regularly exceeding 60 mpg in dense urban areas, it’s among the most efficient gasoline-powered engines in the world — and a glimpse into the future of small hybrid powertrains.
Comparison of Most Efficient Gasoline & Hybrid-Friendly Engines
| Engine | Displacement | Configuration | Vehicles | Fuel Efficiency | Hybrid Support | Efficiency Design Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota 1.8L Atkinson-Cycle (2ZR-FXE) | 1.8L | I4 Atkinson | Prius, Corolla Hybrid, Lexus CT 200h | Up to 58 mpg city | Yes (Toyota Hybrid System) | Atkinson cycle, over 40% thermal efficiency, low-friction design |
| Honda 1.5L i-VTEC Turbo (L15B7) | 1.5L | I4 Turbocharged | Civic, CR-V, HR-V | 36–42 mpg highway | No | Turbocharged, direct injection, variable valve timing |
| Mazda 2.0L SkyActiv-G | 2.0L | I4 Naturally Aspirated | Mazda3, Mazda CX-30 | Up to 41 mpg highway | No | High compression (13:1–14:1), optimized combustion |
| Hyundai 1.6L Smartstream (GDI/MPi Hybrid) | 1.6L | I4 Hybrid | Elantra Hybrid, Kia Niro | Up to 54 mpg combined | Yes (Hybrid) | Dual injection, electric assist, dual-clutch transmission |
| Toyota 2.5L Dynamic Force (A25A-FXS) | 2.5L | I4 Hybrid | Camry Hybrid, RAV4 Hybrid, Lexus ES 300h | Up to 52 mpg combined | Yes (Toyota Hybrid System) | High compression, dual injection, thermal efficiency ~41% |
| GM 1.0L & 1.4L Turbo Ecotec (L3T & LE2) | 1.0L / 1.4L | I3 / I4 Turbocharged | Spark, Sonic, Cruze | Up to 39 mpg highway | No | Small displacement, turbo boost, direct injection |
| Ford 1.0L EcoBoost | 1.0L | I3 Turbocharged | Fiesta, Focus (EU), EcoSport | Up to 40 mpg highway | No | Turbocharged, cylinder deactivation, compact design |
| Toyota 1.5L Dynamic Force (M15A-FXE) | 1.5L | I3 Hybrid (Atkinson) | Yaris Hybrid, Aqua | 60+ mpg real-world (urban) | Yes (Toyota Hybrid System) | Atkinson cycle, e-CVT, 40% thermal efficiency |
Observations and Insights
The highest overall fuel efficiency comes from hybrid systems, with the Toyota 1.5L M15A-FXE leading in urban settings and the Toyota 1.8L 2ZR-FXE excelling in the U.S. Prius. Among non-hybrids, Mazda’s 2.0L SkyActiv-G achieves remarkable results without forced induction, thanks to its high compression and smart combustion design.
Turbocharged small engines like Ford’s 1.0L EcoBoost and GM’s Ecotec 1.0/1.4L offer solid efficiency in compact formats, though they often depend on careful driving to reach advertised numbers. Honda’s 1.5L Turbo (L15B7) shows strong highway economy when not affected by issues like oil dilution.
For drivers prioritizing fuel economy above all else, Toyota and Hyundai’s hybrid systems dominate. However, enthusiasts looking for simpler drivetrains with good real-world returns can still find strong value in Mazda and GM offerings — especially when paired with manual transmissions.
Awards and Recognitions from Leading Automotive Authorities
These engines haven’t just impressed drivers — they’ve also earned accolades from globally recognized institutions for innovation, efficiency, and environmental impact.
| Engine | Organization | Award / Recognition | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota 1.8L Atkinson-Cycle (2ZR-FXE) | Green Car Journal | Green Car of the Year (Toyota Prius) | Multiple (2004, 2010, 2016) |
| Honda 1.5L i-VTEC Turbo (L15B7) | WardsAuto | 10 Best Engines & Propulsion Systems | 2017 (Civic), 2019 (CR-V) |
| Mazda 2.0L SkyActiv-G | WardsAuto | 10 Best Engines (SkyActiv-X variant also awarded) | 2012, 2019 |
| Hyundai 1.6L Smartstream Hybrid | WardsAuto | 10 Best Engines & Propulsion Systems | 2021 (Elantra Hybrid) |
| Toyota 2.5L Dynamic Force (A25A-FXS) | Green Car Journal | Green Car of the Year Finalist (Camry Hybrid) | 2019 |
| GM 1.4L Turbo Ecotec (LE2) | WardsAuto | 10 Best Engines (Earlier Ecotecs) | 2011–2012 (prior variants) |
| Ford 1.0L EcoBoost | International Engine of the Year | Overall Winner, Best Engine Under 1.0L | 2012–2014 (3 years straight) |
| Toyota 1.5L Dynamic Force (M15A-FXE) | Japan Car of the Year (Toyota Yaris) | Technology of the Year (Efficiency & Emissions) | 2020–2021 |
Why Awards Matter
These awards are not just trophies — they reflect years of engineering development aimed at real-world impact. Recognition from sources like WardsAuto signifies breakthroughs in combustion efficiency, emissions reduction, and integration with hybrid systems. Meanwhile, Green Car Journal and Car of the Year awards emphasize sustainability and market relevance, affirming each engine’s success both technically and commercially.

